- Details
On 15 June 2020, the National Statistics Office of Georgia published its annual publication for the agricultural sector - Agriculture of Georgia 2019. The publication shows that agriculture, forestry, and fishing comprised 7.2% of the nominal GDP in 2019, slightly lower than the 7.8% share in 2018, but in line with the general trend over the last five years (on average 7-8% of GDP). In nominal terms, the output of agriculture increased by 4% in 2019 compared to 2018. In real terms agriculture, forestry, and fishing contributed 7.4% to the GDP in 2019, lower than its contribution of 7.9% in 2018. Regarding changes in the output of the sector, the real output declined by 4% in 2019 compared to 2018. Though, the share of income from the sale of agricultural production in the total income of households did not change from 2018; which stood at 5.5% and amounted to a monthly average of 60.3 GEL.
- Details
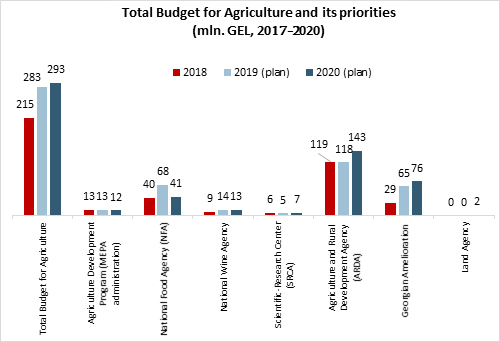
On December 10, the parliament of Georgia approved the state budget for 2020. The budget includes allocations of around 14.4 billion GEL. Out of which, the Ministry of Environmental Protection and Agriculture (MEPA) will receive 353 mln. GEL (2.4% of the total budget allocation). MEPA will direct approximately 293 mln. GEL (2.0% of the total budget allocation) towards agricultural development and 60 mln. GEL (0.4%) will be spent on environmental protection.
Compared to 2019, the budget for agricultural development will increase by around 4%. More state funds will be allocated to the Scientific-Research Center (SRCA), the Agriculture and Rural Development Agency (ARDA) and Georgian Amelioration, while the budget will slightly decrease for the National Food Agency (NFA), the Agriculture Development Program (MEPA administration), and the National Wine Agency.
- Details
On 30 August 2019, a public hearing to discuss Georgia’s Rural and Agricultural Development Strategy for 2021-2027 was conducted at the Ministry of Environmental Protection and Agriculture (MEPA). The new strategy document represents a roadmap for Georgia’s rural and agricultural development for the next decade.
The strategy outlines three major goals to be achieved by 2027:
1. Increasing the competitiveness of agricultural and non-agricultural sectors;
2. Sustainable management of natural resources, preservation of ecosystems, and climate change adaptation;
3. Ensuring food/feed safety and the development of efficient veterinary and plant protection systems.
- Details
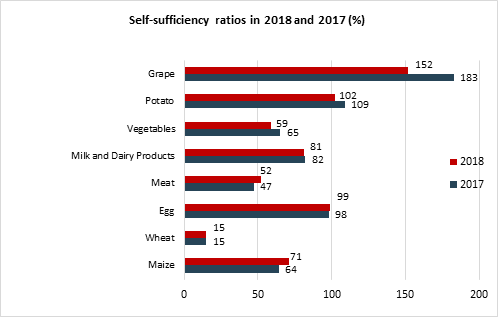
The share of the rural population in the total population decreased slightly, from 42.6% in 2015 to 41.3% in the beginning of 2019. The share of agriculture in total GDP has also declined, from 9.1% in 2015 to 7.7% in 2018. While production figures have gone up, there was a 6.4% increase in agricultural production in 2018 compared to the previous year. Production in the plant-growing sector increased by 10.9%, and animal production experienced an increase of 2.1% compared to 2017. Looking at the self-sufficiency ratio, the highest decrease was for grapes, followed by vegetables, and the highest increase was for meat, followed by maize.