Sadly, today we are using budget funds to directly fund unemployment. We are financing professions that may not be required later.
Giorgi Kvirikashvili, Prime Minister of Georgia
As most other former socialist countries, Georgia enjoys a very high literacy level, as measured e.g. by the share of people completing secondary education. And yet, the single most problematic factor for doing business in Georgia, at least since 2013, is “inadequately educated workforce”. Not crime. Not corruption. Not access to finance. Not faulty infrastructure. Inadequately educated workforce.
Table 1: The most problematic factors for doing business in Georgia since 2007
| 2007 | Policy Instability |
| 2008 | Access to financing |
| 2009 | Access to financing |
| 2010 | Access to financing |
| 2011 | Access to financing |
| 2012 | Access to financing |
| 2013 | Inadequately Educated Workforce |
| 2014 | Inadequately Educated Workforce |
| 2015 | Inadequately Educated Workforce |
| 2016 | Inadequately Educated Workforce |
Source: World Economic Forum, The Global Competitiveness Reports
Importantly, the problem is not so much about access to education per se but access to the right kind of education and, most importantly, high quality Vocational Education and Training (VET). Equally disturbing is the other side of this coin: youth unemployment, particularly high (about 30% in 2016) among those aged 20-24.
So, what do we do to tackle this problem?
One possibility is to revolutionize the VET system and dramatically improve the quality of vocational training and education offered by Georgian public and private college. Sounds like the right thing to do, except that Georgian youth don’t really want to be trained for what they perceive to be low paying, manual jobs. As one employer put it in a public discussion forum, “all Georgians want to become economists and measure the country’s GDP. Nobody wants to actually work and contribute to the GDP”.
Clever technicians and people with great manual skills can actually earn a lot of money, even in Georgia. Our challenge is that many Georgian boys (and girls) don’t want to go into vocational training for reasons that have nothing to do with their future occupations and earnings. First, there is the issue of social status. Second, young Georgian males would do anything to defer and completely avoid military conscription, an option reserved only for university students, under Georgia’s current laws. Third, universities offer better networking opportunities and a far superior marriage market. “How do you become a general’s wife”, asks Liudmila in the Soviet 1980 classic Moscow does not believe in tears. The response she got was “You marry a young lieutenant”.
The challenge of over-education is not unique to Georgia. It is rooted in the truly global phenomenon of ‘degree inflation’ whereby a very large share of youth is trapped into at least trying to get a college degree (any). The logic is very simple. If everybody, even people of very modest academic abilities, have a college degree, not having one comes with a stigma.
In the run up to the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis, ever increasing prices lured people into buying a piece of real estate even when they could not repay their debt. Today, many Americans of subprime means and subprime academic abilities are trapped into mortgaging their lives in order to finance college degrees that serve no purpose other than avoiding a social stigma. Some economists believe that the fast accumulating mountain of student debt will be the next big financial bubble.
In Georgia, the problem of over-education is compounded by the fact that access to (useless) higher education is very easy. The revenue stream of Georgian universities depends only on one thing: the number of students they enroll. Not research productivity. Not teaching quality. Not students’ learning outcomes or their employability. Just the number of tuition-paying students. It is therefore not surprising that universities set very low admissions standards and implement very loose screening in the course of one’s studies. Effectively, universities and students strike a deal: universities pretend to be teaching, and students pretend to be studying. As my 12-year old daughter would say, easy peasy lemon squeezy.
Furthermore, university degrees are not only easy to get. They are also affordable. The fees charged by Georgian universities (about $900/year) may be not within reach for many Georgian families. However, those who can afford private tutors may qualify for a government scholarship. And because class attendance is neither required, nor monitored, the opportunity cost of acquiring a university degree is extremely low. Most students, the most employable among them, start their professional careers while in the 2nd or 3rd year of studies.
Most crucially, the “pretence” equilibrium in the Georgian education market is very stable. Diploma mills are not sanctioned for not delivering education or skills. Georgian employers in any case prefer to hire candidates with a higher education degree (any). And it cannot be otherwise in an environment in which even taxi drivers and shop assistants brandish a university diploma (or two).
HOW ABOUT MAKING VOCATIONAL EDUCATION MORE ATTRACTIVE?
The Georgian government’s goal, as specified in its 4-point plan, is to remake the entire VET landscape: phase out outdated class-based learning by aging VET professors and introduce the so-called dual education model that is practiced in countries like Germany, Austria and Switzerland. The concept of dual education stems from the centuries-old apprenticeship tradition surviving to this day in many parts of Western Europe. According to this model:
• VET students are employed as apprentices by private companies for the entire duration of their education. In fact, their enrolment is conditioned on being hired!
• Furthermore, about 70-80% of the students’ learning objectives are achieved through on-the-job training, while only 20-30% are acquired through classroom instruction.
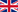
• As apprentices, students are paid a modest salary or stipend, which together with the cost of training/mentorship, exceeds their productivity in the early training phase. The costs of training (for the companies) are more than fully recouped later, when apprentices acquire the basic skills of their profession.
This model of VET education is supposed to be allowed and, indeed, encouraged by Georgia’s new laws on VET and Public-Private Partnerships. But, is it feasible in the current Georgian context?
Figure 1: The economics of industry-led VET education: the costs incurred by employers in the early phase of a student’s apprenticeship are covered by gains achieved once the student achieves a basic level of qualification
It is crucial to understand that the German and Swiss companies are willing to incur the cost of training because students do not “defect” to competing companies in the middle of an apprenticeship (without acquiring a formal qualification). And students do not defect because all companies in the sector hire either young apprentices or people with a formal professional qualification.
Yet, Georgia is not Switzerland. Georgian businesses are very young, and the Georgian business community is not very well organized. The incentives for Georgian businesses to engage in expensive industry-led VET are not very strong, to put it mildly. Particularly, in the absence of German-style coordination.
The situation has been very well characterized by Nikora CEO Irakli Bokolishvili: “Skills are definitely a bottleneck for us”, said Bokolishvili at a recent ISET-hosted seminar. “We tried to hire graduates of the Agrarian University but they have not seen meat in the life. At the same time, businesses are not “training centers”. If I train people, how can I be guaranteed that they stay with me? A good specialist can easily find a job elsewhere.”
* * *
Let us make two practical suggestions.
In recent years, the Georgian government has undertaken a number of important legal steps to allow private sector companies to develop and run dual education programs. Yet, though necessary, such steps are not sufficient. In the absence of relevant traditions, the government should be willing to engage in a serious coordination effort, strengthening and, in some cases creating, sectoral business associations, empowered to decide on relevant qualification standards and be involved in the governance and management of VET programs. One can start in a small way by piloting the model in one or two sectors in which coordination among leading actors may be easiest to achieve (construction?).
Second, Georgia may be proud of its success back in 2005 in implementing tough policies to eliminate corruption and restrict supply of low quality ‘higher education’. It introduced unified university admission examination and withdrew licenses from more than a hundred of ‘degree mills’ or village universities (orghobis universiteti), as they were called in Georgian. Time may have come to take further steps: raise the mandatory threshold for university admission; set a higher minimum tuition fee to further narrow the field; condition public scholarships on means testing in addition to NAEC exam scores; put universities and VET college on a level playing field when it comes to military conscription.
Provided political will is there, such measures are likely to have an immediate and significant impact.














Comments
The dual education model is widely practiced in the Commonwealth (53 countries, 2.4 billion people) and the USA as well. The medieval trade guilds of England and the other countries of the UK were the origin of this.
The military service deferment is easily fixed but parliamentarians dont wish their kids to serve, preferring the poor and ethnic minorities to do the heavy lifting. Abolition of deferment, combined with NATO standard training of national servicemen in communications, engineering, electrical engineering, transport and logistics, would yield young people with some sound technical fundamentals that can be used in trades or professions later on. IT would also shift the demand away from humanities degrees for young men and towards trades.
A major disincentive to taking a trade is the unregulated nature of trades in Georgia. Why spend 3-4 years as an electricians apprentice when some half-trained clown standing outside Iliava Market will claim to be a sparkie and work for peanuts, competing with you? Every year hundreds of Georgians die as a result of carbon monoxide poisoning and electrocution in the home due to shoddy work done by untrained personnel. At least there is a regulation now to compel homeowners to use a trained gas system installer from the gas company, instead of a local handyman, but it is still widely flaunted and the penalties for breaking the rules are insignificant.
Trades impacting upon human health and safety should be the first to be regulated. A clear timeline of imposition of regulations needs to be broadcast, following which jail terms will be imposed for unlicensed operators breaking the rules. A grace period whereby EU-standard trade schools offer these courses in a flexible and affordable manner, with multiple campuses in the country available, needs to be put in place so existing uncertified operators can upgrade their skills and new apprentices can move through the system to the market as tradesmen. Gas system installation and electrical trades are the first that come to mind.
I could not agree more, Simon. Those trades/professions that impact human health and safety should be given the highest priority, as part of a pilot
In a developed service economy with limited natural resources and an ageing population (Hong Kong), there are 36,000 VET students per million head of population every year. Georgia has only 5400 VET students per million head of population; not even enough to meet existing demand let alone future requirements.
Another issue poorly understood by the public is the Life Long Learning approach to vocational training and education in most developed and developing countries. One may start as a 17 year old apprentice and be licensed as a journeyman at age 20-21, but it is quite normal these days for tradesmen not only to do additional specialist technical courses, but to upgrade their qualifications from certificate to diploma, associate degree or bachelor degree at a later stage in their career. They will often get credit on some subjects due to previous trade school classes and professional experience. In many cases, their employer funds it for them, seeing it as a useful investment in turning a skilled tradesmen into a manager. This might happen when the candidate is in their 20s or 30s.
So, just because you dont have a degree at 21 does not mean you will never have one, and moving from a trade to industrial management is really very common.
Western multinationals are still paying six-figure USD annual salaries to expatriate tradesmen in Georgia because of the lack of skilled labour, particularly master tradesmen. If we get training and regulation right here, there is scope to develop lucrative and respectable trades for Georgian people while removing bottlenecks to our development.